1 复旦大学信息学院电磁波信息科学教育部重点实验室,上海 200433
2 鹏城实验室,广东 深圳 518055
3 上海低轨卫星通信与应用工程技术研究中心,上海 200433
4 上海市低轨卫星通信技术协同创新中心,上海 200433
可见光通信因其显著优势逐渐成为星间通信的研究热点。可见光通信能够提供丰富且无需授权的频谱资源,传输速率高,保密性强以及抗电磁干扰等。可见光激光通信器件发射功率较高、抗辐照能力强、激光束散角小,有望应用于星间大容量长距离通信链路传输。实现了集成的40路波分复用可见光激光通信系统,复用29个可见光波长,采用离散多音比特加载调制和Levin-Campello算法,达到了418.3 Gbit/s的总传输数据。针对可见光激光通信系统中的带宽受限和高频衰落的问题,该系统采用了数字预均衡技术,根据该系统的信号特点,设计了相应的佐贝尔网络,通过增强高频信号能量和减小低频信号能量实现整体通信性能的提升。实验表明,数字预均衡可显著提升可见光激光通信性能。该系统证明了可见光激光通信在星间大容量通信中的巨大潜力。
波分复用 激光通信 可见光通信 卫星通信 激光与光电子学进展
2024, 61(7): 0706002

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory for Information Science of Electromagnetic Waves (MoE), Department of Communication Science and Engineering, Fudan University, Shanghai 200433, China
2 National Institute of LED on Silicon Substrate, Nanchang University, Nanchang 330096, China
In recent studies, visible light communication (VLC) has been predicted to be a prospective technique in the future 6G communication systems. To suit the trend of exponentially growing connectivity, researchers have intensively studied techniques that enable multiple access (MA) in VLC systems, such as the MIMO system based on LED devices to support potential applications in the Internet of Things (IoT) or edge computing in the next-generation access network. However, their transmission rate is limited due to the intrinsic bandwidth of LED. Unfortunately, the majority of visible light laser communication (VLLC) research with beyond 10 Gb/s data rates concentrates on point-to-point links, or using discrete photodetector (PD) devices instead of an integrated array PD. In this paper, we demonstrated an integrated PD array device fabricated with a Si-substrated GaN/InGaN multiple-quantum-well (MQW) structure, which has a array of micro-PD units with a common cathode and anode. This single-integrated array successfully provides access for two different transmitters simultaneously in the experiment, implementing a MIMO-VLLC link at 405 nm. The highest data rate achieved is 13.2 Gb/s, and the corresponding net data rate (NDR) achieved is 12.27 Gb/s after deducing the FEC overhead, using 2.2 GHz bandwidth and superposed PAM signals. Furthermore, we assess the Huffman-coded coding scheme, which brings a fine-grain adjustment in access capacity and enhances the overall data throughput when the user signal power varies drastically due to distance, weather, or other challenges in the channel condition. As far as we know, this is the first demonstration of multiple visible light laser source access based on a single integrated GaN/InGaN receiver module.
Photonics Research
2024, 12(4): 793
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Although the 5G wireless network has made significant advances, it is not enough to accommodate the rapidly rising requirement for broader bandwidth in post-5G and 6G eras. As a result, emerging technologies in higher frequencies including visible light communication (VLC), are becoming a hot topic. In particular, LED-based VLC is foreseen as a key enabler for achieving data rates at the Tb/s level in indoor scenarios using multi-color LED arrays with wavelength division multiplexing (WDM) technology. This paper proposes an optimized multi-color LED array chip for high-speed VLC systems. Its long-wavelength GaN-based LED units are remarkably enhanced by V-pit structure in their efficiency, especially in the “yellow gap” region, and it achieves significant improvement in data rate compared with earlier research. This work investigates the V-pit structure and tries to provide insight by introducing a new equivalent circuit model, which provides an explanation of the simulation and experiment results. In the final test using a laboratory communication system, the data rates of eight channels from short to long wavelength are 3.91 Gb/s, 3.77 Gb/s, 3.67 Gb/s, 4.40 Gb/s, 3.78 Gb/s, 3.18 Gb/s, 4.31 Gb/s, and 4.35 Gb/s (31.38 Gb/s in total), with advanced digital signal processing (DSP) techniques including digital equalization technique and bit-power loading discrete multitone (DMT) modulation format.
GaN-based LED LED array VLC V-pit sidewall quantum well high-frequency response Opto-Electronic Science
2023, 2(5): 230005
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory for Information Science of Electromagnetic Waves (MoE), Fudan University, Shanghai 200433, China
2 Shanghai Engineering Research Center of Low-Earth-Orbit Satellite Communication and Applications, Shanghai 200433, China
3 Shanghai Collaborative Innovation Center of Low-Earth-Orbit Satellite Communication Technology, Shanghai 200433, China
4 National Institute of LED on Silicon Substrate, Nanchang University, Nanchang 330096, China
5 Peng Cheng Laboratory, Shenzhen 518055, China
6 e-mail:
7 e-mail:
8 e-mail:
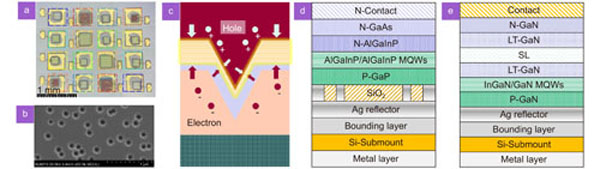
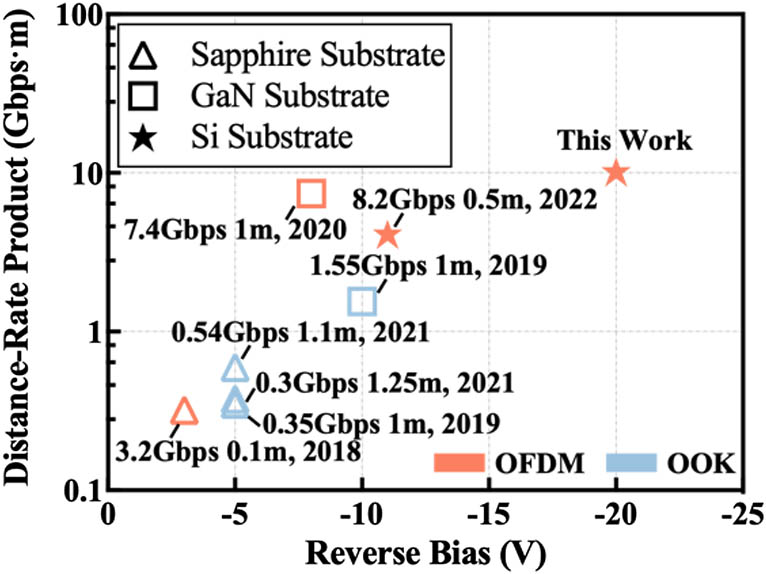
Visible light communication (VLC) has emerged as a promising communication method in 6G. However, the development of receiving devices is much slower than that of transmitting devices, limited by materials, structures, and fabrication. In this paper, we propose and fabricate an InGaN/GaN multiple-quantum-well-based vertical-structure micro-LED-based photodetector (μPD) on a Si substrate. A comprehensive comparison of the photoelectrical performance and communication performance of three sizes of μPDs, 10, 50, and 100 μm, is presented. The peak responsivity of all three μPDs is achieved at 400 nm, while the passband full-widths at half maxima are 87, 72, and 78 nm for 10, 50, and 100 μm μPDs, respectively. The cutoff bandwidth is up to 822 MHz for 50 μm μPD. A data rate of 10.14 Gbps is experimentally demonstrated by bit and power loading discrete multitone modulation and the proposed digital pre-equalizer algorithm over 1 m free space utilizing the self-designed 50 μm μPD array as a receiver and a 450 nm laser diode as a transmitter. This is the first time a more than 10 Gbps VLC system has been achieved utilizing a GaN-based micro-PD, to the best of our knowledge. The investigation fully demonstrates the superiority of Si substrates and vertical structures in InGaN/GaN μPDs and shows its great potential for high-speed VLC links beyond 10 Gbps.
Photonics Research
2022, 10(10): 2394
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory for Information Science of Electromagnetic Waves (MoE), Department of Communication Science and Engineering, Fudan University, Shanghai 200433, China
2 Peng Cheng Laboratory, Shenzhen 518055, China
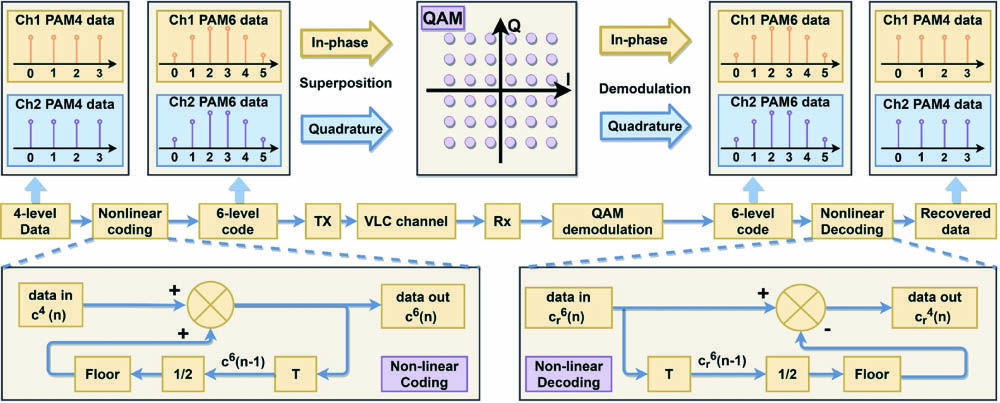
In this paper, we propose a 36-quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM) superposition modulation technique that is featured with uneven symbol probability by nonlinear precoding, named nonlinear coded nonuniform superposition (NCNS) QAM. Its aim is to alleviate the nonlinearity effect caused by high instantaneous power in multi-input single-output (MISO) visible light communication (VLC) system, with an uneven probabilistic-shaped constellation. The transmitter includes two LEDs to send signals independently, and the receiver uses a photo detector to receive the superposed QAM signal. The experiment results show that NCNS has a better robustness against nonlinearity than pulse amplitude modulation 4, approximately gaining a 16% increase in maximum usable peak-to-peak voltage and a 33% enlargement in dynamic range area. It is a simple but effective approach to solve the bandwidth limits related to signal power and hopefully be applied in large power VLC systems such as underwater VLC, or to improve the robustness against power fluctuation.
visible light communication light-emitting diode multi-input single-output quadrature amplitude modulation nonlinear coding spectral shaping Chinese Optics Letters
2022, 20(4): 042501





